Risk Management
Our ERM approach
Our risk management systems are robust with a well-developed risk management framework governed by mandated board and management committees with the relevant expertise. Our risk measures seek to balance regulatory requirements and shareholder expectations for risk-adjusted returns. We carefully manage our capital, liquidity, and funding levels to support business growth, maintain depositor and creditor confidence, and create value for all our shareholders. We take a holistic, forward-looking view of the risks we face, assessing both the prevalent and emerging threats in our operating environment. Our well-developed framework supports a consistent approach to enterprise risk management.
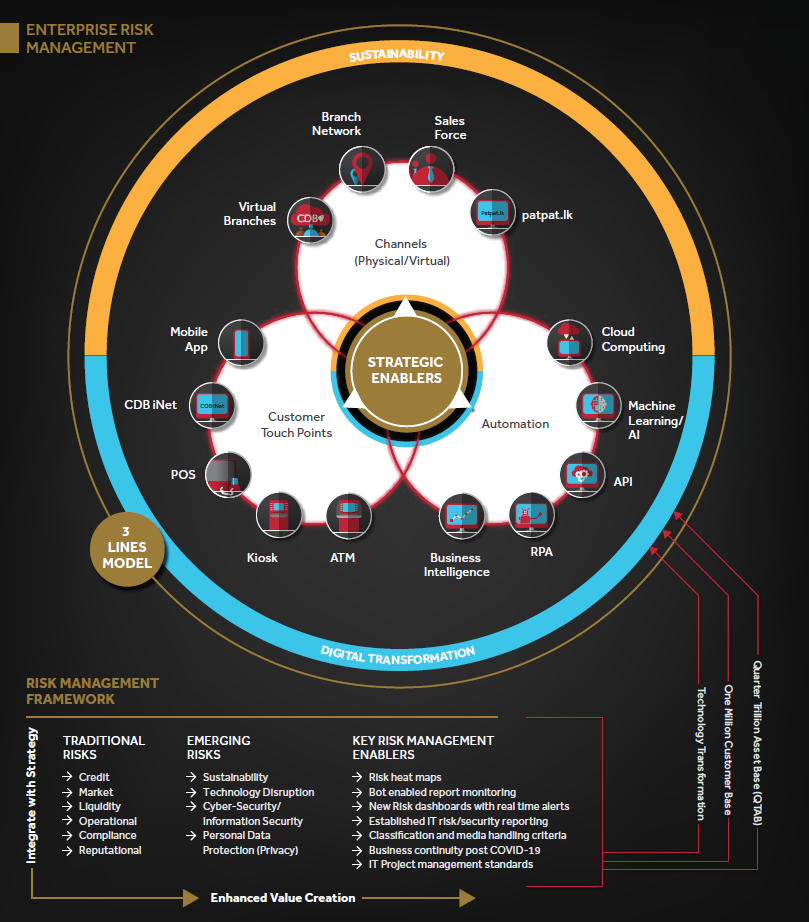
As depicted above, our ERM framework has been established in line with CDB’s entity-wide strategic objectives and values with the ultimate objective of enhanced value creation. It ensures that risk management at CDB is not only a mere exercise of recognising risks but it also helps the Company to harness opportunities arising from the evolving environment. This future focused approach and robust governing structure (3 lines model) ensure CDB’s resilience amidst both traditional risks and emerging risks through key risk management enablers which are integrated with high level strategies as well as mid and bottom level operations.
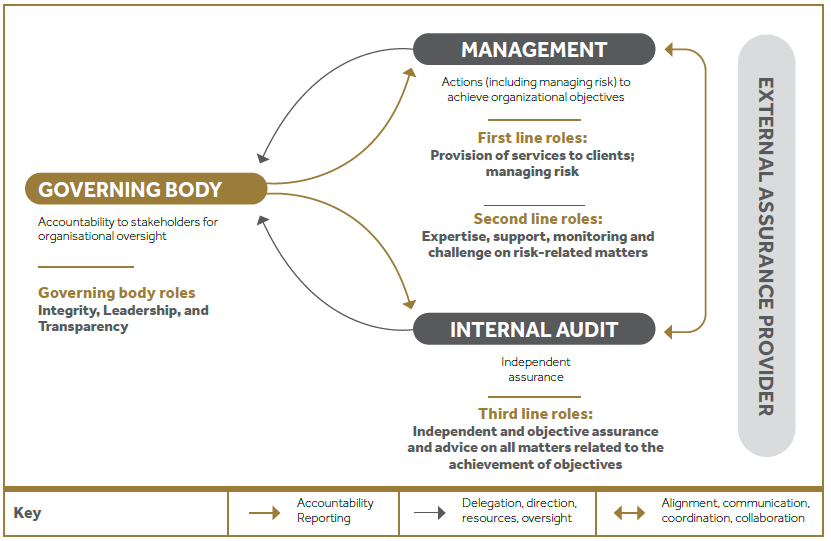
CDB’s three lines model clearly defines the roles and responsibilities for the management of risk within the Company. This emphasises the fundamental concept that risk ownership and management is everyone’s responsibility from the Board to the business units.
First line under “Management” leads and directs actions/ resources to achieve organisational objectives and maintains continuous communication regarding management of risks with governing bodies (BOD/Executive Committees). Further, this line is responsible for establishing and maintaining appropriate structure and processes for the management of operations and associated risks.
Second line is expected to provide complementary expertise, support, monitoring, and challenge the first line relating to the management of risk. Further, it also provides analysis and reports on the adequacy and effectiveness of risk management (including internal controls). This layer represents the risk and compliance division of CDB.
The role of the Third line is played by the Internal Audit division and they mainly provide independent and objective assurance and advice to management and the governing body on the adequacy and effectiveness of governance and risk management (including internal control) to support the achievement of organisational objectives and to promote and facilitate continuous improvement.
Our risk culture
We actively promote a risk-minded culture across the organisation. CDB risk culture provides guiding principles for the behaviours expected from our people when managing risk. We encourage the following behaviours and outcomes:
- An enterprise-level ability to identify and assess current and future risks, openly discuss them, and take prompt actions (CDB Assurance net)
- The highest level of integrity by being transparent and proactive in disclosing and managing all types of risks
- A constructive and collaborative approach in providing oversight and challenge, and taking decisions in a timely manner
- Everyone to be accountable for their decisions and feel safe in using their judgment to make these considered decisions
- Risk identification and risk management are widely discussed topics whenever the management is going ahead with a new product, process etc.
We acknowledge that financial services industry inherently involves risk-taking and undesired outcomes will occur from time to time; however, we shall take the opportunity to learn from our experience and formalise what we can do to improve. We expect all our people to demonstrate a high awareness of risk and control by self-identifying issues and managing them in a manner that will deliver lasting change. What is unique about CDB is how we have carved the importance of risk identification and risk management into our team members’ mindset. For them, it is a value addition more than a mere reporting activity. We reward those team members who identify and report on critical risk areas and we have embedded such risk identification as an evaluation criteria to all our team members’ performance assessment scorecards as well. We recognise our people as “Risk Reporting Champions” at the annual awards ceremony and award them with magnificent monetary and non-monetary rewards.
A summary of the year in review from risk perspective
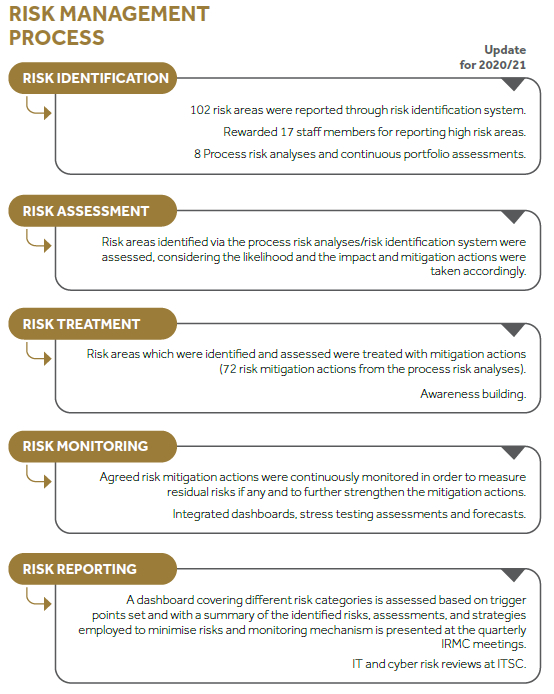
The Board of Directors is integrally involved in ensuring stringent management of risk, liquidity, capital, and conduct through our risk appetite framework which continues to be assessed in light of prevailing market conditions and CDB’s overall strategy. The primary aim is to achieve a suitable balance between risk and reward in our business. Although the current macro-environment due to the COVID-19 pandemic continues to present significant challenges, CDB was able to record exceptional performance and risk metrics throughout the year in review. While industry gross NPL ratios averages around 11%, we were able to manage the same at 7% level amidst all the challenges. Sri Lankan economy recorded a GDP contraction of 3.6% in 2020 and expectations for a strong rebound in 2021 are likely to be impacted by the vulnerabilities stemming from the third wave of the pandemic currently engulfing the South Asian region. We remain highly focused on managing credit, liquidity, market, reputational, and operational risks. IT risks and cyber security are high priorities as we are a true believer in embracing technology, and CDB continually aims to strengthen systems and controls in order to manage cyber risks. Concerns over money laundering, terrorism financing, fraud, and corruption are growing and our compliance team has ensured that we meet all our regulatory obligations in this regard.
Given the unusual and unprecedented economic and market conditions as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the risk outlook remains uncertain and it is unclear how our clients and stakeholders will adjust over the coming months. As the pandemic evolves, management is focused on maintaining the integrity of our balance sheet through continuous oversight of credit, liquidity, and capital risk with ongoing stress testing, scenario planning, and ensuring the business remains operational through resilient strategies implemented, as we continue to support our clients during this period. We are comfortable that we have a strong balance sheet with regard to the high levels of liquidity and strong capital as well as established risk management processes and systems in place to navigate through this period of uncertainty.
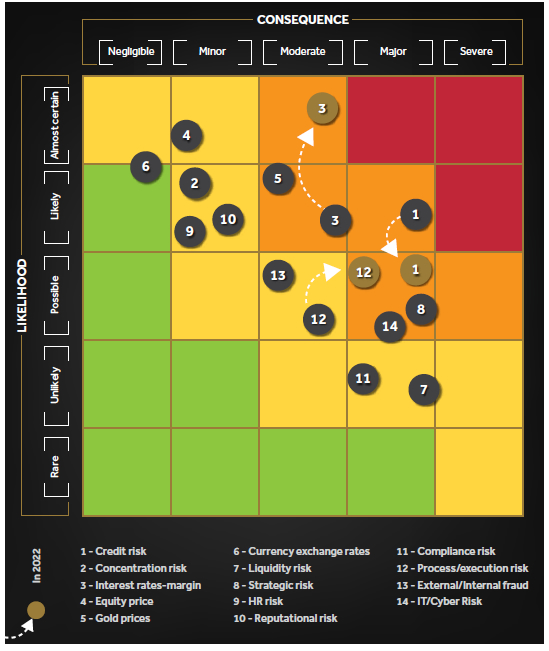
Future outlook
CDB proactively manages risk and continually identifies emerging issues that could pose an impact to its business in the future. The Risk Heat Map below shows the key risk drivers that could affect the Company in FY2021/22 (over a one year horizon) along the dimensions of probability and impact. The risk drivers are not to be seen in isolation as they may trigger or reinforce each other.
Snapshot of Key Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Credit riskLosses arising from the failure of obligors to meet their financial or contractual obligations when due. |
||
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus | |
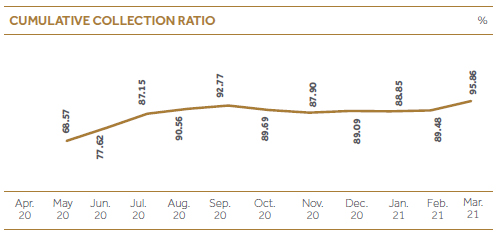
| NPL ratio was managed at 7% compared to previous year’s 7.54%, where industry ratio was at 11%. Under the tough environment that prevailed, many strategies were put in place through recovery team to maintain healthy collection ratios, particularly after the first and second COVID waves. Cumulative collection ratio stood at 95.86% compared to 92.35% in the last financial year.
Moratoriums were granted as per the CBSL stipulated guidelines and were monitored with high emphasis. Reducing yard stocks too was given a high emphasis via allocating resources to dispatch high number of vehicles on a daily/weekly basis. Yard stock reduced by Rs. 780 Mn. compared to last year. NPL ratios were monitored giving high priority and exposures were reduced for the products with continuous high NPL ratios. Collections were monitored under different baskets and different perspectives. |
Plan to continue with the initiated strategies to manage NPL ratios within acceptable levels and the potential impact of them adhering to SLFRS 9. NPLs to be monitored giving special consideration on products, sector etc. to identify products/sectors which are prone to high NPLs. Obtain the business intelligence support and improve automated processes focusing on recoveries through enhanced systems, processes, and analytics. | |
Funding and liquidity riskFailure to maintain or generate sufficient cash resources to meet day-to-day obligations |
||
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus | |
| Due to the impact of COVID, CBSL reduced the statutory liquidity ratios and the market continued to have excess liquidity throughout the financial year. Statutory liquidity ratio stood at 14.19% as at 31 March 2021. All obligatory payments were met during the pandemic even with low collection figures while offering moratoriums to customers. | To maintain adequate liquid assets while focusing on maximising the return. Focus on having optimum liquidity level to ensure compliance with statutory ratios and that the Company has the appropriate diversification and tenor of funding and liquidity. | |
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus |
| Maturity mismatch was prevailing around -3% (1 year cumulative) and was managed at tolerable levels. Liquidity stress testing was done based on different worst case scenarios and liquidity contingency plans were prepared and discussed. A weekly Treasury meeting was conducted focusing mainly on cash flow predictions to ensure we meet the short-term obligations. Off-shore options for funding were evaluated and Company could attract EUR 5 Mn. worth of funding through foreign borrowings. | To conduct cash flow predictions/liquidity stress testing and to be better prepared for unforeseen risks. |
Market riskThe risk of loss arising from a change caused by adverse movements in market interest rates, commodity prices, equity prices, and currency exchange rates. |
||
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus | |
| SDF rate was decreased by 175bps by the CBSL causing a positive impact on net interest income. Lending rates were also decreased in order to facilitate economic recovery but CDB was able to maintain adequate margins throughout the year by having right balance in the asset mix. Reviewed maturity mismatches and stress testing was conducted and presented at monthly ALCO meetings based on CBSL guidelines of both behavioural and contractual maturities. At monthly ALCO meetings, interest rates predictions, margins, asset liability composition, weighted average rates etc. were reviewed. Gold prices were monitored on a daily basis and stress testing was carried out to assess the impact of continuous price reductions. A weekly gold price dashboard was communicated to the senior management which consisted of gold price movements, trends, tenor exposures, profit margins etc. | Conduct gold price & portfolio analysis to set optimum advances to minimise market risk. Continue to conduct interest rate stress testing under different scenarios to better react to unforeseen economic conditions. Continue to monitor and manage market risk elements in the context of future volatile market environment, including monetary policy decisions and rate changes. | |
Operational riskThe risk of loss resulting from inadequacy of, or failure in internal processes or events including internal frauds processes or events including internal fraud, external fraud, employment practices and workplace safety, clients, products, business practices, damage to physical assets, business disruption and systems failures, execution, delivery, and process management. |
||
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus | |
| New ways and means of onboarding customers, immediate credit approvals, opening of savings accounts through automated processes were initiated while complying with regulatory guidelines.
Investments made on technology infrastructure enabled our customers to conduct their financial transactions without any hassle while staying at home during the lockdown period.
Shifting to more IT enabled platforms also exposed us to IT/Cyber risks where we increased the numbers of vulnerability reviews through the help of third parties and staff members were continuously made aware of identifying cyber threats.
CDB team placed 5th position of the drill on readiness for cyber defence conducted by TechCert. Exceptional reports obtained via Oracle BI to monitor transactions were strengthened to monitor online transactions. The CDB team is provided with proper in-house training, external training, and virtual training based on the training needs identified at the performance appraisals. |
Enhancing IT governance framework.
Strengthen the security measures by keeping the existing systems up to date with the latest protection software and timely updates in order to prevent from the external threats.
Facilitate RPA processes to emphasise less human interactions and improvement of performance and establishing segregation of duties.
Enhancing credit/debit card Fraud Risk Monitoring with dashboards with behaviour analysis. Frequent vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to ensure the systems are resilient to cyber-attacks. Initiate information security awareness among the staff members in light of the increased use of digital platforms and work from home practices. |
|
Strategic RiskThis is the risk that the future business plans and strategies are inadequate to prevent financial loss or protect the Company’s competitive position and shareholder returns. |
||
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus | |
| With challenging market conditions, achieved a bottom line growth of 39%. With the dawn of another decade, CDB has launched its new strategic direction and business plan to be a technologically sound best corporate citizen. In line with the strategic objectives, many process automation projects were initiated and the proposals were referred to risk division and were evaluated covering various risk categories. Various dashboards in place to monitor the performance on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis and various sensitivity analyses and financial analyses are carried out at ALCO, finance committee meetings etc. to ensure Company is on track to achieve the targets set. | To use data and BI data & analytics for better decision making.
Continue to adapt our ways of working, skills base, and human resource practices to meet the requirements of a different future.
Continue to align business strategy and Enterprise Risk Management strategy to proactively identify risks and to minimise any negative impact to CDB. |
|
Reputational riskDamage to the Company’s image due to potential or actual events which may impair the profitability and/or sustainability of business. |
||
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus | |
| Implementation of toll free ‘Missed call service’ to encourage customers to share their feedback (suggestions & complaints) with Customer care agent. Existing IVR was developed to identify priority customers with urgent requirements (e.g.: lost card). Adhered to ‘Work from Home’ contingency plan due to COVID-19 outbreak and maintained 24×7 operations with trilingual support. Implemented “Customer Information Retrieval Solution” which will allow the agents to provide a better and a speedy solution to the client inquiries. | Continue to expand customer awareness about the missed call service to improve customer engagement on the process. Advance IVR development to automate frequently asked questions. To enable customer portfolio summary to pop up in agents’ desktops via a CRM pop-up screen when a customer contacts the Hotline via a system registered number. | |
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus |
| Strengthen the Customer verification Matrix (Low/Medium/High risk verification) based on customer inquiry to identify the original customer. Training and development programmes were conducted through external professional trainers for contact centre agents to improve their knowledge and capabilities on delivering a quality customer service. Contact centre was switched to working from home environment with the breakdown of the pandemic and was able to deliver the same level of service to customers without any operational interruptions. | Continue to enhance product knowledge and improve service quality of contact centre agents through more activities and training & development programmes. |
Compliance RiskGRI 205-1, 205-2, 205-3 The risk of legal or regulatory sanction, financial loss, or damage to reputation the Company may suffer as a result of its failure to comply with laws, regulations, codes of conduct, and standards |
||
| Key highlights in 2020/21 | Future focus | |
| Appointment of compliance representatives for each and every department including branch staff and frequent discussions with them has led to a creation of compliance culture throughout the organisation. Continuous training programmes, Quiz Sessions along with QR Code E-Flyers to all staff with special focus to Branch Staff have created good awareness on Compliance including Anti Money Laundering aspects. Continuous transaction monitoring with several red flag indicators is conducted in order to identify unusual and suspicious transactions. | To have an automatic alert generation system for both compliance and transaction monitoring in order to create real time alerts. Effective online training and awareness sessions with the support of E-Learning platforms. Generating an interface with KYC data for all customers which would create a path for enhanced due diligence on customers and some other critical decision making activities. | |
Key Risks VS Mitigation Strategies
Credit Risk
Navigating an unprecedented slowdown in economic activity as a result of the pandemic put significant strain on maintaining our loan book and credit quality of portfolios.
Default Risk
Default risk materializes from losses stemming from the failure of clients to meet their financial obligations to the Company.
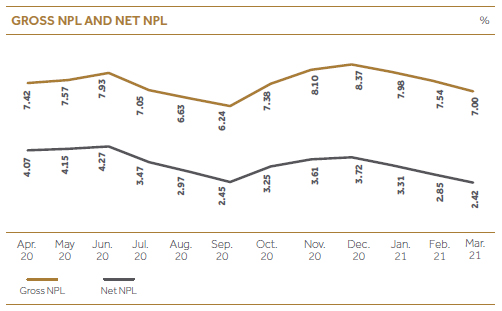
As mentioned earlier, asset quality in the LFCs sector rapidly deteriorated due to the impact of the pandemic on the economy during the year under review. However, CDB was able to maintain its NPL ratio within an acceptable level as evident from the ratio of 7.00% (gross) as of 31st March 2021 compared to the industry average of 11.3% by Mar 2021. Excluding repossessed stock, ratio was still better at 6.39% (gross). The value of the repossessed stock was brought down by 67% during FY2020/21 to below Rs. 500 Mn. level. And, the net NPL ratio excluding revolving repossessed stock was a mere 1.7%. We were able to maintain an outstanding cumulative collection ratio of 95.86% during the year despite the tough economic and market environment.
Stress Testing: Impact on capital adequacy ratio (CAR) and non-performing loans (NPL) ratio of the Company from the changes in NPLs (Non-performing loans)
| Base Case | |
| Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR %) | 15.34 |
| Capital Base (Rs'000) | 13,800,144 |
| Total Risk Weighted Assets (Rs.'000) | 89,961,825 |
| NPL Ratio (%) | 7.00 |
| Total Non Performing Assets (Rs'000) | 5,412,289 |
| Total Performing Assets (Rs'000) | 71,951,760 |
Impact on Company’s Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) from the Changes in NPLs (Non-Performing Loans)
| Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | |
| Magnitude of Shock (%) | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Total NPLs (Rs'000) | 5,412,289 | 5,412,289 | 5,412,289 |
| Increase in NPL (Rs'000) | 270,614 | 541,229 | 811,843 |
| Revised Capital (Rs'000) | 13,529,530 | 13,258,915 | 12,988,301 |
| RWA (Rs'000) | 89,961,825 | 89,961,825 | 89,961,825 |
| Revised CAR (%) | 15.04 | 14.74 | 14.44 |
A 5% shock on the capital base due to an increase in NPLs will reduce the CAR to 15.04%.
Impact on Company’s NPL ratio from the Changes of NPLs
| Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | |
| Magnitude of Shock (%) | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Total NPLs Portfolio (Rs'000) | 5,412,289 | 5,412,289 | 5,412,289 |
| Increase in NPL (Rs'000) | 270,614 | 541,229 | 811,843 |
| Revised NPLs (Rs'000) | 5,682,903 | 5,953,518 | 6,224,132 |
| Total Loan Portfolio (Rs'000) | 77,364,049 | 77,364,049 | 77,364,049 |
| Revised NPL ratio (%) | 7.35 | 7.70 | 8.05 |
NPL ratio will increase from 7.00% to 7.35% if NPLs increased by 5%.
Managing Default risk
As a response to the COVID-19 outbreak, we refined our credit risk management practices as well as credit standards to meet the changing economic environment. While providing flexible solutions to the customers for repayments amidst pandemic hit on their income streams, we ensured that a sufficient return gets generated without making any impact on our cash inflows/ collections. Overdue waive off campaign, Voucher campaign, Moratorium relief loan campaign, Internal incentive campaign and Reschedulements were the some of the strategies put in place, which helped us to successfully manage our NPLs during the year. Supporting top management in making optimum decisions relevant to lending products, detailed analyses were carried out on the lending portfolio by the Credit Evaluation and the Risk Divisions with the support of BI unit on a continuous basis.
Recovery performance was continuously monitored at management committees throughout the year, setting targets for each month in terms of collections and NPLs and different strategies were adopted to collect due amounts based on age baskets. Age bucket movement has been a key area which was thoroughly monitored in managing NPLs apart from first three rentals collection ratio for newly onboarded customers. Such performance was discussed in detail at monthly ALCO meetings and quarterly IRMC meetings, leading to strategic decisions that improved performance.
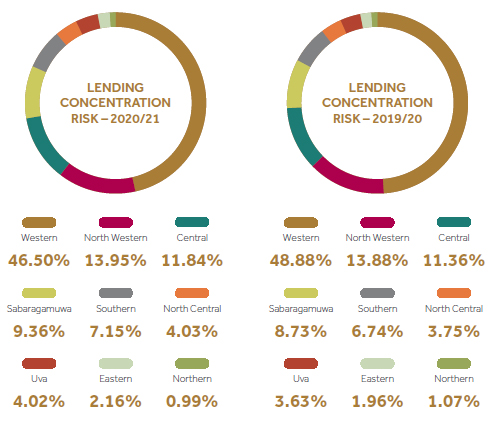
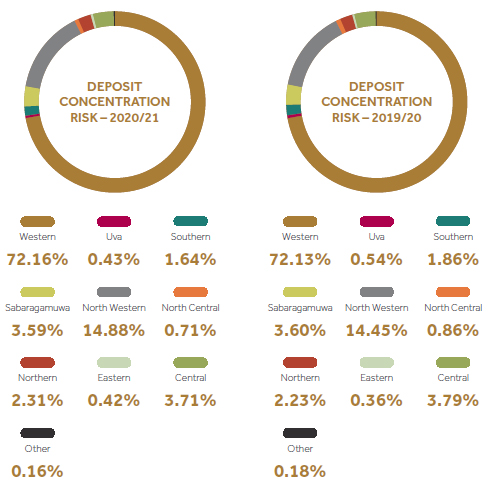
Concentration risk
Concentration risk may materialize as a result of significant exposure to a group of counterparties whose likelihood of default is high. Group of counterparties could be segmented based on a particular product, geography, sector etc. to ascertain concentrations.
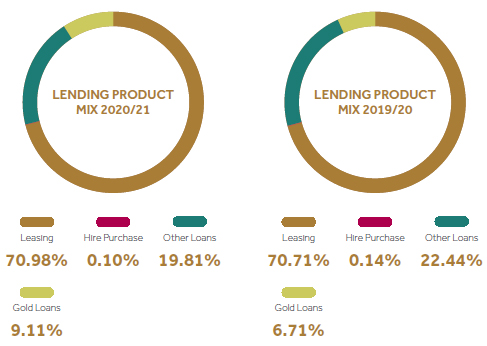
If we consider the lending product mix, considerable increase is shown in the gold loans.
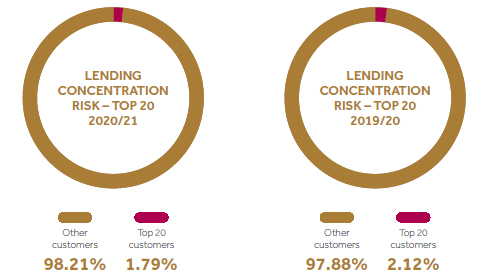
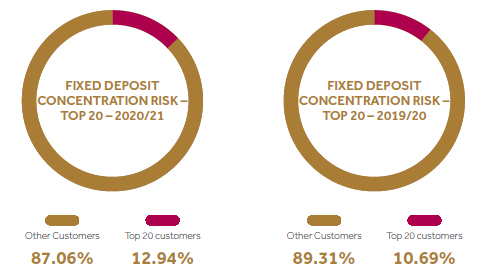
Top 20 customers represent only 3% of the total lending portfolio.
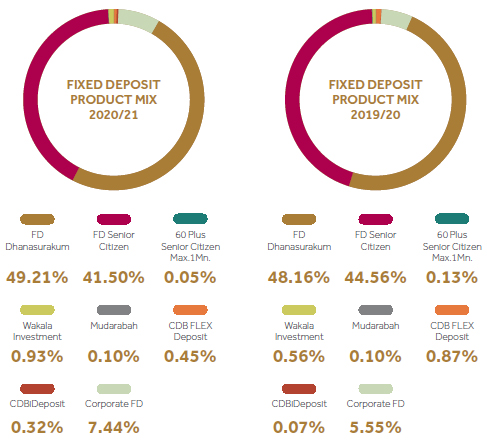
Company’s fixed deposits portfolio is highly concentrated on Dhanasurakum and Deegayu Senior citizen products.
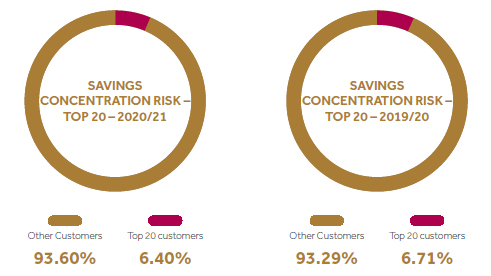
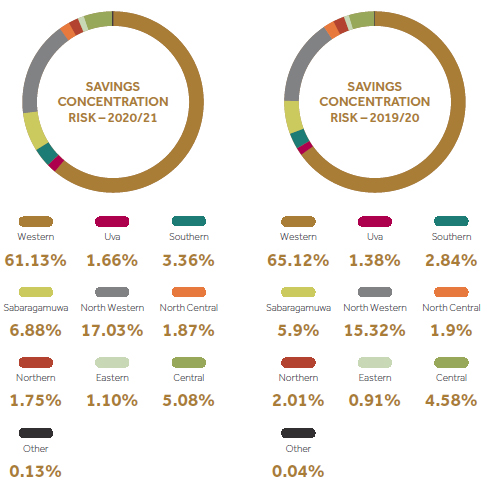
Managing concentration risk
With an attempt to reduce CDB's exposure to vehicle segments, more focus was given to differentiate our product portfolio by driving gold related lending, credit card segment, margin trading product and newly introduced green related lending product. Monthly vehicle related disbursements were prevailing above 90% level continuously in the past but currently it is below 90%. This has been an area closely being monitored at quarterly IRMC meetings.
Credit Risk Trigger Points
| Criteria | Target Level | Current Position (as at 31-03-2021) | Risk Exposure Compared to 2019/20 |
| NPL ratio | Below 5% | 7.00% | [[Arrow icon]] |
| Cumulative Collection ratio | >95% | 95.86% | [[Arrow icon]] |
Market Risk
The risk of a change in the market value, actual or effective earnings, or future cash flows of a portfolio of financial instruments, including commodities, caused by adverse movements in market variables such as equity prices, bond and commodity prices, currency exchange rates and interest rates, correlations and implied volatilities in all of these variables.
Interest rate risk
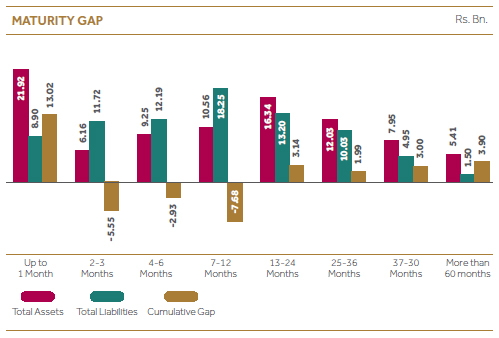
Market-driven interest rates can adversely affect our profitability and the value of our balance sheet financial instruments. These instruments include loans, debt securities, certain trading-related assets and liabilities, deposits, borrowings and derivatives. Fluctuations in interest rates will result in re-pricing of our liabilities faster than interest earning assets as majority of our liabilities are short term in tenure which is evident from maturity gap.
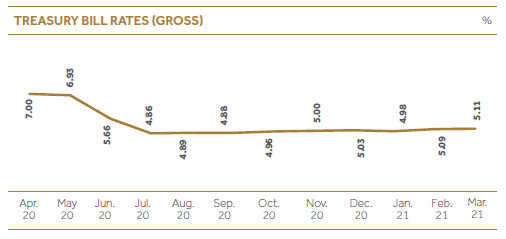
Managing Interest rate risk
Interest rate movement is one of the main aspects evaluated at the ALCO meetings. Forecast on WALR, WABR and Margins is one of the exercises carried out to evaluate the potential impact of stressed scenarios (market interest rate increases) and possible impact on NII also is accessed at the same forum. Suitable re-pricing decisions on lending products are made based on expected interest rate risk exposure movements.
Equity Price risk
Equity price risk can be defined as potential risk of the fair value of equities falling as a result of fluctuations in market prices of shares. CDB has invested in a share portfolio comprising different stocks relating to different industries thus exposing the Company to equity price risk.
Managing equity price risk
We ensure that we have invested in a diversified portfolio by setting approved company-wise and sector-wise exposure limits. Our dedicated corporate finance team continuously monitors market price movements and optimum purchase and selling decisions are made based on top management approvals.
Commodity price risk
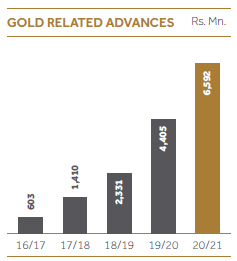
This is considered as another main risk CDB is exposed to because of the rapidly increasing Gold Loan portfolio. Currently Gold related lending accounts for approximately 7% out of the total assets. During FY2020/21, gold market prices reached all time high levels of above 2,000 USD per Ounce in August with the global uncertainties caused by COVID-19 pandemic.
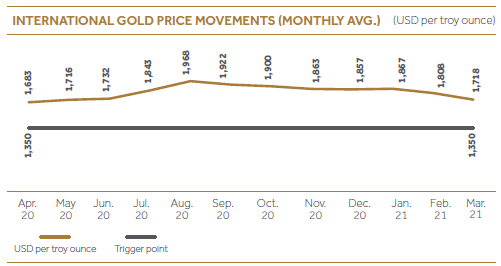
Stress Testing: Impact on gold loan portfolio due to the decrease of gold loan prices
| Base case | |
| International Gold price average March 2021 ($ per troy ounce) | 1,718 |
| Gold loan portfolio (Rs. '000) | 6,592,073 |
| Existing Portfolio LTV | 80.00% |
| Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | |
| Magnitude of shock (%) | 5 | 10% | 15% |
| Price after shock ($ per troy ounce) | 1,632 | 1,546 | 1,460 |
| Portfolio LTV after shock (%) | 84.09 | 88.65 | 93.73 |
Managing Commodity Price risk
During FY2020/21, Gold loans portfolio experienced an increase of 50% compared to the previous financial year end portfolio and reached Rs. 6.6 Bn. In line with the fluctuation in International gold prices and competitor gold advance levels, CDB adjusts advance levels based on a comprehensive risk assessment which is mainly based on expected profit margin, LTV and expected market price movements. As market prices are extremely volatile, we continuously keep an eye on market price movements and immediate actions are taken as and when required. Such information is discussed in a detailed manner at monthly ALCO meetings.
Exchange rate risk
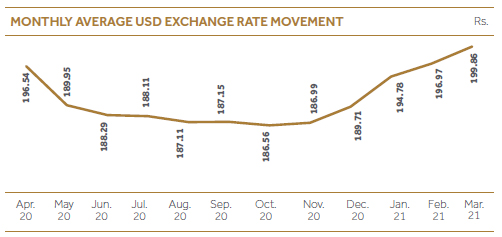
Exchange rate fluctuations are having an impact on the value of foreign currency related assets and liabilities. We are engaged in the business of money exchange and as a result, hold a significant amount of foreign currency in hand. Further, it is very important that we have a considerable quantum of foreign loans in our funding structure. Accordingly, an exchange rate movement mainly in USD/LKR rate can be expected to cause a significant impact to our bottom line. During FY 2020/21, we have seen a significant increase in USD/LKR exchange rate (LKR depreciation) with the COVID-19 pandemic impact on the country’s economy.
Managing Exchange Rate Risk
For managing the potential losses resulting from adverse movements in exchange rates, CDB has adequately covered foreign currency exposures through hedging with external parties. Exchange rates are monitored on a regular basis and optimum decisions are made as and when required.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the possibility that, despite being solvent, sufficient capacity to fund increases in assets is not available, or the Company is unable to meet payment obligations as they fall due, without incurring unacceptable losses. COVID-19 pandemic has been the main challenge during the year under review limiting cash inflows and increasing the uncertainty of experiencing sudden cash outflows (Retail deposits and Savings).
| Direction | As at 31st March 2021 | As at 31st March 2020 |
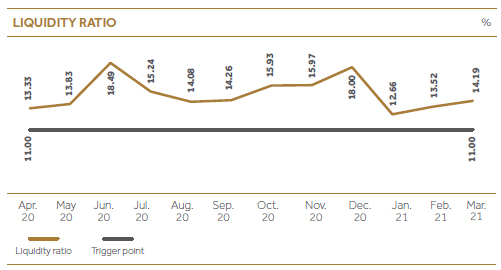
| Maintain minimum holding of liquid assets based on the outstanding value of the time deposits mobilized by the Company (%) | 14.19 | 15.28 |
| Required minimum amount of liquid assets (Rs. ‘000) | 3,201,119 | 3,362,939 |
| Available amount of liquid assets (Rs. ‘000) | 7,361,866 | 8,674,662 |
Stress testing: Impact on liquid assets ratio due to a fall in deposit liabilities
| Base Case | |
| Liquid Assets Ratio (%) | 14.19% |
| Liquid Assets (Rs'000) | 7,361,866 |
| Total Deposit Liabilities (Rs.'000) | 51,890,388 |
Impact on Liquid Assets Ratio due to a fall in Liquid assets
| Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | |
| Magnitude of Shock (%) | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| Liquid assets (Rs'000) | 7,361,866 | 7,361,866 | 7,361,866 |
| Deposit Liabilities (Rs'000) | 51,890,388 | 51,890,388 | 51,890,388 |
| Fall in Liquid Assets | 294,475 | 588,949 | 883,424 |
| Revised Liquid Assets | 7,067,391 | 6,772,917 | 6,478,442 |
| Ratio after shock (%) | 13.62 | 13.05 | 12.48 |
A 12% shock will reduce liquidity ratio to 12.48%.
Managing Liquidity Risk
At CDB we always give our priority in meeting contractual obligations and for that, we ensure that sufficient funding levels are maintained by continuously monitoring and managing liquidity position efficiently and effectively while generating an optimum return on our liquid assets portfolio. Cash flow position and forecasts are regularly reviewed by top management under different stressed scenarios based on maturity mismatch analysis to ensure that we are capable of maintaining stakeholder confidence. Contingency funding plans are designed to ensure a positive outcome in the event of a liquidity crisis. Liquid Assets Ratio is considered as a key indicator in risk dashboard which was discussed in detail at IRMC meetings. Despite all the challenges caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, CDB was able to maintain liquid assets levels well above the statutory requirements while meeting all the obligations and investing on business growth as well.
Market Risk Trigger Points
| Criteria | Target Level | Current Position (as at 31-03-2021) | Risk Exposure Compared to 2019/20 |
| Liquid Assets Ratio (%) | 10 | 14.19 | [[Arrow icon]] |
| Maturity Gap of 1 year bucket (%) | Below 10 | (3.33) | [[Arrow icon]] |
Operational Risk
Operational risk is direct or indirect loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. This definition covers a myriad of non-financial risks, including conduct risk, fraud, cyber, privacy, unauthorized lending/borrowing activities and information security.
There are seven types of operational risks given below that banks and financial institutions should bring in to focus:
| Risk Type | How we manage |
| Internal Fraud – Unexpected financial, material or reputational loss as a result of fraudulent actions of persons internal to the Company. |
|
| External Fraud – Impact arising due to fraudulent activities committed by parties external to the Company. |
|
| Employment Practices and Workplace Safety – Non-compliance to ethical practices related to employment or health-and-safety laws and regulations. |
|
| Clients, Products, and Business Practice – Risk of engaging in malpractices which are against the interests of our stakeholders such as market manipulation, improper way of doing business, over promise & under delivery, misuse of confidential information etc. |
|
| Damage to Physical Assets – Potential losses arising due to damages to physical assets as a result of natural disasters or terrorist activities. |
|
| Business Disruption and Systems Failures – Disruptions and threats to business continuity due to power failures, software failures, hardware failures etc. |
|
| Execution, Delivery, and Process Management – Not meeting service standards due to human errors and process omissions. |
|
Other Risks
Reputation risk
Reputational risk can be defined as “the risk of damage to the trust of our customers, employees, authorities, investors, partners and the general public have in CDB, with the potential for adverse financial or non-financial impact”. As a public deposit taking institution, reputation or the Company’s image is one of a most important aspects which needs to be taken into consideration for resilience against the competition.
Managing reputational risk
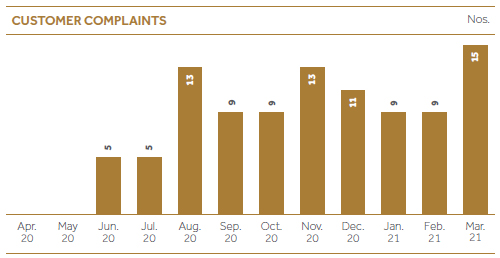
CDB risk management framework covers the process through which active decisions are taken on matters which may pose a reputational risk, before such risk materializes, and, in doing so, prevent damage to CDB reputation, wherever possible. While every employee has a responsibility to protect our reputation, the primary responsibility for the identification, assessment, management, monitoring and, if necessary, referring or reporting, of reputational risk matters lies with our business divisions. Each employee is under an obligation, within the scope of his or her activities, to be alert to any potential causes of reputational risk and to address them according to the Framework. Among business divisions, our contact center ensures an effective and efficient process in dealing with customer complaints/ concerns in order to deliver a superior customer service and to manage reputational risks as well as working as a key part of the Company in risk identification process. Customer complaints are one of the key indicators which is used to assess and manage reputational risk at quarterly IRMC meetings. CDB is in the process of automating customer complaints and feedback handling mechanism through a centralized system ensuring that each and every complaint and/or feedback gets escalated to one place from all the customer contact points with the expectation of establishing an improved follow up and solution providing mechanism.
Strategic risk
Strategic risk may materialize due to lack of adaptability to the changing business context, wrong decisions, poor planning etc. The financial services industry is currently in a period of heightened change and uncertainty. Changing regulatory expectations and increasing geopolitical risk are shaping the external environment, while growing competition among banks, non-banking finance institutions, and financial technology firms (FinTechs) is reshaping the competitive landscape.
Managing strategic risk
Financial and non-financial performance is monitored and evaluated at ALCO, Finance Committee meetings and other special meetings on a monthly basis and for that, there are many dashboards with KPIs which help the top management to ensure that the Company is on track to achieve short term and long term targets. From a risk point of view, a set of KRIs related to strategic risk are monitored on a quarterly basis at IRMC meetings and significant variances are discussed in a detailed manner.
To ensure that product/ process initiations are in line with Company’s risk appetite and strategic direction, internal processes are defined and followed to obtain risk sanctioning/ recommendation prior to senior management approval on the same. Being a tech-savvy organization, we always embrace change and streamline our processes and products continuously adopting and investing on bringing latest technology with the expectation of providing a superior service to our customers.
People risk
At CDB, we presume people risk as loss of skills, talent and knowledge to the organization in a way of employee turnover or lack of skilled human resources which is required to efficiently and effectively achieve Company’s goals and objectives. We consider our employees as the most valued asset and always help them to realize their full potential.
Managing people risk
Performance appraisals are carried out biannually to identify staff skill requirements and to assess their performance which ultimately helps to determine training requirements. We not only enrich our people with knowledge through in house trainings, but also help them to improve their skills through external trainings as well as foreign trainings which are conducted by renowned persons in relevant fields. Beyond job related trainings, we conduct various other events and programs such as sports day, new year festival, talent show, awards day etc., to promote work life balance and to make the Company a better place to work. We promote an open door policy where our employees are allowed to raise any matters/concerns directly even with the MD/CEO at any given time.
Compliance risk
Over the past decade, the financial services industry has faced not only an exceptional growth but also unprecedented changes and challenges, resulting in a slew of compliance regulations. In recent years, as governments and regulators attempt to combat money laundering, terrorist financing and other illicit financial transactions, regulations have proliferated both globally and locally, in step with increasing stakeholder expectations for safe and secure operations. Across the spectrum, laws, regulations, policies and standards are rapidly evolving and continue to represent the biggest overall enterprise risk.
Managing compliance risk
By ensuring that all the applicable rules, laws and regulations are observed, we are committed to protect our customers and, in general, all of our counterparties and employees. Complying with these commitments is not only the responsibility of a few experts, but of all employees, who must demonstrate compliance and integrity in their daily tasks. Accordingly, we have adopted an organization and a body of strict doctrines, procedures and rules that are updated regularly. And for that, CDB has proactive ongoing engagements with the relevant regulatory and government authorities.
Our compliance division ensures that Company conducts its business in line with all applicable statutory and legal requirements while continuously monitoring changes in the legal environment and compliance requirements imposed by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka and other authorities. Applicable rules which need to be adhered to and compliance requirements are communicated to top management at compliance meetings which are held on a monthly basis and it makes a ground to discuss on plans and strategies put in place in order to meet potential compliance requirements.
| Criteria | Target Level | Current Position (as at 31-03-2021) | Risk Exposures Compared to 2019/20 |
| Capital Adequacy –Tier I | % | 12.10 | [[Arrow icon]] |
| Capital Adequacy – Tier I & II | % | 15.34 | [[Arrow icon]] |
| Capital Funds to deposit liabilities | % | 28.16 | [[Arrow icon]] |
Environmental and Social risks
Impact of our business to community and environment may cause either positive or negative implications as a whole in return. As a carbon neutral entity, we are committed and realign our strategies as required to preserve our environment and deliver maximum value to our stakeholders enhancing people’s standard of living.
Managing Environmental and Social risks
Environment and Social Risk Management System which was implemented in consultation with Climate Smart Initiatives (Pvt) Ltd (Climate SI) is the platform which ensures that we identify and efficiently manage our exposure to environmental and social risks associated with our services to the community. To enhance our capacity to manage aforesaid risk areas, our credit evaluation system was re-engineered improving the screening of high-risk facilities covering environmental & social aspects.
Information and Cyber risks
In order to execute on innovation while maintaining trust in the digital economy, financial institutions need to pursue two parallel strategies - cyber risk agility and resiliency. Cyber risk agility is essential to build a flexible cyber risk framework that can anticipate and prepare for innovations that bring longer-term success. Cyber risk resiliency on the other hand enables us to withstand potential cyber risk events from these innovations and keep the business moving toward its goals. Information and cyber security is an area with an increased risk profile across financial services. We continue to invest and enhance our capability in information and cyber security through the expansion and strengthening of our operating model as adoption to new technology in alignment with competitive environment exposes us to cyber and information risks.
How we manage Information and Cyber risks
All technological improvements are subject to comprehensive testing mechanisms and we have elevated information and cyber security by obtaining ISO 27001 international standards on information security. We strengthen the security measures by keeping the existing systems up to date with the latest protection software and timely patch updates in order to protect them from external threats. We initiate information security awareness among the staff members in light of the increased use of digital platforms and work from home practices due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conduct and culture risk
Risk culture can be considered as a system of values and behaviours present in an organization that shapes risk decisions of management and employees. Improper, unlawful or unethical behaviour or action that may have a negative impact on an organization’s clients or counterparties or the fair and effective operation of the industry can be considered as conduct risk.
How we manage conduct and culture risk
Customer protection framework introduced by the CBSL will form an avenue for us to focus more on mitigating conduct risk. We have grown a risk culture where staff members tend to report risks which is enriched with a rewarding framework going in line with the whistle-blowing policy. CDB’s approach to conduct risk management is essential to the way we do our day-to-day business. It is based on sustainable practices and integrated in how staff manage their responsibilities and conduct themselves.


